Distributed File System & Cloud Storage
Distributed File System (DFS)
Definition:
- A DFS is a file system distributed across multiple servers or locations, allowing programs to access or store files as if they were local.
Purpose:
- Enables users of physically distributed systems to share data and resources using a common file system.
Key Features:
- Transparency:
- Location Transparency: Users don’t need to know the physical location of files.
- Structure Transparency: No need for clients to know the number or locations of file servers.
- Access Transparency: Local and remote files are accessible in the same manner.
- Naming Transparency: File names do not indicate file locations.
- Replication Transparency: Copies of files on multiple nodes are hidden from users.
- User Mobility:
- User’s home directory is automatically accessible from any node.
- Performance:
- Should be similar to that of a centralized file system.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use:
- Simple user interface with a small number of commands.
- High Availability:
- Continues to function in case of partial failures (link, node, or storage drive failures).
- Scalability:
- System grows easily as the number of nodes and users increase.
- High Reliability:
- Minimizes data loss with backup copies.
- Data Integrity:
- Ensures correct synchronization of concurrent access requests using concurrency control.
- Security:
- Implements mechanisms to safeguard information from unauthorized access.
- Heterogeneity:
- Supports multiple computer platforms.
File System Replication:
- Early iterations used Microsoft’s File Replication Service (FRS).
- Windows Server 2003 R2 introduced DFS Replication (DFSR), improving FRS by copying only changed portions of files and compressing data to minimize network traffic.
Standalone vs. Domain-based DFS Namespace:
- Standalone DFS Namespace: Exists on the local computer, not using Active Directory. Limited advantage and rarely used.
- Domain-based DFS Namespace: Stores DFS configuration in Active Directory, accessible via domain name.
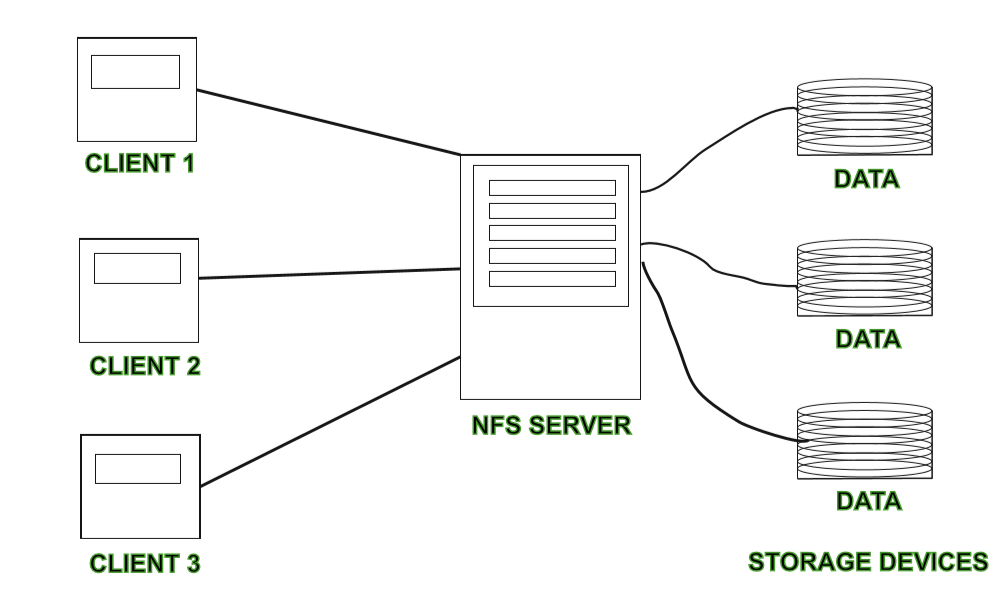
Advantages:
- Allows multiple users to access/store data.
- Enhances data availability, access time, and network efficiency.
- Provides data transparency even if servers or disks fail.
Disadvantages:
- Security concerns due to the need to secure nodes and connections.
- Possible data/message loss during network movement.
- Complicated database connection and handling compared to single-user systems.
- Risk of overloading if all nodes send data simultaneously.
Cloud Storage
Definition:
- Cloud storage is a virtual locker for data, allowing remote storage and access through the internet.
Key Features:
- Greater resource availability.
- Easy maintenance.
- Large network access.
- Automatic systems.
- Enhanced security.
Types of Storage Systems:
- Block-Based Storage System:
- Like traditional hard drives, allowing partitioning and formatting of volumes.
- File-Based Storage System:
- Accessed via a network, typically using NAS devices.
- Pre-formatted and partitioned, mapped to local drive letters.
- Object-Based Storage System:
- Uses HTTP protocols for storing objects in containers without hierarchy.
Cloud Storage Architecture:
- Consists of distributed resources functioning as one.
- Durable through versioning and replication.
- Users pay based on actual usage, reducing capital expenses.
- Energy-efficient and secure, often disaster-proof.
Advantages:
- Scalability: Easy expansion of capacity and performance.
- Flexibility: Data manipulation and scaling according to needs.
- Simpler Data Migrations: Eliminates disruptive data migrations.
- Recovery: Access to files even if local hardware fails.
Disadvantages:
- Requires reliable electricity and internet.
- Limited support, especially for free versions.
- Dependency on internet connection.
- Slow networks can hinder access.
Benefits for Businesses:
- Saves space and money by eliminating on-premises data storage infrastructure.
- Simplifies hardware and software maintenance.
- Enhances employee collaboration and remote work capabilities.
- Reduces energy consumption, benefiting the environment.